Congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is completely treatable, but untreated, can cause serious and permanent health problems.
Syphilis
Syphilis is an infection that has largely been eradicated due to antibiotics and condoms. But, you can still catch it if you are having unprotected sex in some areas of the world.
EVENT CLOSED Event: Women & their Microbes
Women & their Microbes was a huge success last year with over 90 participants from over nine countries. This time the theme is reproduction, with the one-day event covering hands-on workshops and lectures from leaders in the medical and scientific community.
Study: How early life circumstances affect menarche and menopause
We examine a review of how childhood experiences impact menarche and menopause.
Cystic fibrosis and vaginas, sex, and fertility
Cystic fibrosis can seriously affect your sex life, vagina, and reproductive system, but it doesn't mean it's the end of your sex life or happy vagina.
Reifenstein syndrome
Reifenstein syndrome is an androgen insensitivity syndrome occurring in foetal development that results in improper sex organ development in boys.
Vaginal agenesis – absent vagina
Vaginal agenesis is the complete absence of a vaginal canal, caused by an interruption to normal development as a foetus. Reconstruction is a viable option in most cases.
Reasons you don’t have your period yet
If your period has never come, and you are older than 15, then you need to have some investigations done into why not.
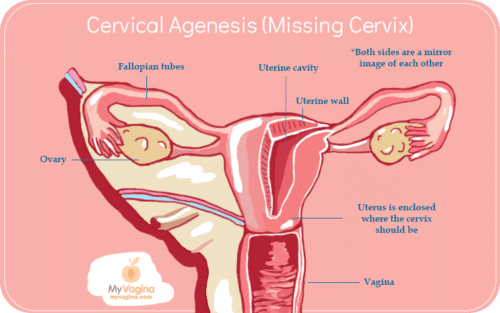
Cervical agenesis
Cervical agenesis means the cervix - connecting the uterus and vagina - is absent, usually due to either surgical removal or an anatomical abnormality that occurred during development in the womb.
Cervical stenosis
Cervical stenosis is the narrowing - for whatever reason - of the cervix, the neck of tissue that joins the vagina and uterus. A narrow cervix can create a few issues with in-and-out flow between the uterus and the vagina, including sperm, periods and babies.
Swyer syndrome (XY gonadal dysgenesis, XY female)
Swyer syndrome means you are a chromosomal male (46, XY), but - aside from ovaries - the rest of you is 100% woman. This means you look and feel just like a woman, but your chromosomes say you are a man.
MRKH syndrome
MRKH syndrome is a congenital abnormality, whereby the uterus, top part of the vagina, and cervix do not exist or are very small. Ovaries are usually normal, since the ovaries run off a different system.
Staphylococcus bacterial biofilms
Staph biofilms have been found on regular-use tampons and pads (after use).
Vaginal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection
MRSA is an antibiotic-resistant form of Staph that can infect the vagina. It can be life-threatening.
Shigella vaginal infections
Shigella is a cause of vaginal infections and vulvovaginitis, particularly in children.
Vulvar, vaginal and perineal injuries
Injuries to the vagina, vulva and perineum vary in their severity and the impact the damage has on the pelvic structures. Injuries range from straddle injury to urethral damage to deep pelvic trauma.
Vulvovaginitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae in children
H. influenzae is a common cause of vulvovaginitis in children, but it may not be easily detected by a GP or standard cultures.
Gynaecology in children and babies
We briefly overview the vulva and vagina from a developmental perspective - what to expect.
Differences of Sexual Development (DSD)
DSD is the multitude of in-between typical male and female presentation we see in human bodies. The variations range from typically female with every physiological twist and turn to typically male.
5-alpha-reductase deficiency (5 ARD)
5 ARD is a genetic blip that blocks the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in a growing foetus. DHT is required for the penis and testicles to develop in a male foetus, resulting in ambiguous genitalia. People with 5 ARD may be brought up as girls or boys.